
Mastering Face Grooving Essentials with Tungaloy
This article elucidates crucial insights into both selecting optimal face grooving tools and mastering the key principles of face grooving itself, providing indispensable guidance for precision machining.
Table of Contents
1. Selecting the Right Tools: Face Grooving and Lateral Feed Machining
- Essential guidelines for selecting tools tailored to face grooving and lateral feed machining, guaranteeing precision and efficiency in your machining endeavors
2. Essential Insights: Key Points for Face Grooving Mastery
- Precision Positioning: Machining Techniques for Face Grooving
- Horizontal Feed Machining: Maximizing Efficiency and Accuracy
Clamp-on grooving tools are the preferred option for end face grooving and cross feed machining due to their versatility and precision. Additionally, the screw clamp type is well-suited for machining small diameter end face grooves. Self-clamping types also offer compatibility for these applications, ensuring a comprehensive range of options for varying machining needs. It’s important to select the most suitable breaker depending on the tool path to maintain effective chip control during face grooving.
Tungaloy´s recommendations:
Edge grooving tools feature distinct shapes compared to other grooving tools, often incorporating a curvature to prevent interference with the workpiece body. Consequently, precise tool selection and setup are paramount to ensure optimal performance. Following this insight, let’s explore essential considerations for executing end face grooving operations, focusing on factors critical to achieving precision and efficiency.
Precision Positioning: Machining Techniques for Face Grooving
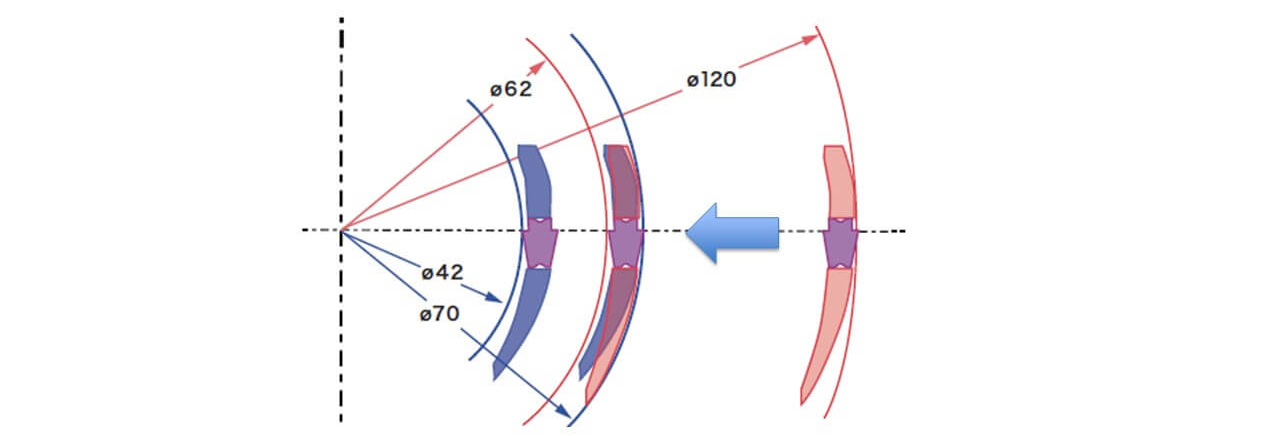
In face grooving, it’s crucial to adhere to the specified minimum and maximum machining diameters. Straying outside of these ranges can result in body interference issues, compromising the effectiveness of the machining process. Maintaining awareness of these diameter limits is essential for ensuring smooth and successful operations.

Horizontal Feed Machining: Maximizing Efficiency and Accuracy
Key Considerations for Tool Selection and Machining Methods:
- Verify the maximum diameter of the face groove. Opt for a tool capable of accommodating the maximum diameter for face grooving.
- Initiate the face groove processing from the point where the maximum diameter is attained.
- Following groove machining, execute cross-feeding towards the interior of the diameter.
Understanding the Rationale Behind the Recommended Method:
- In face grooving, machining with a larger curvature facilitates superior chip evacuation.
- Tools with larger diameters suitable for face grooving boast expanded jaw areas on the insert’s bottom, resulting in heightened tool rigidity. Enhanced tool rigidity fosters stability during cross-feed machining or face grooving processes, ensuring consistent and reliable performance.




