Kraftvolle Schaftfräser mit hervorragender Leistung
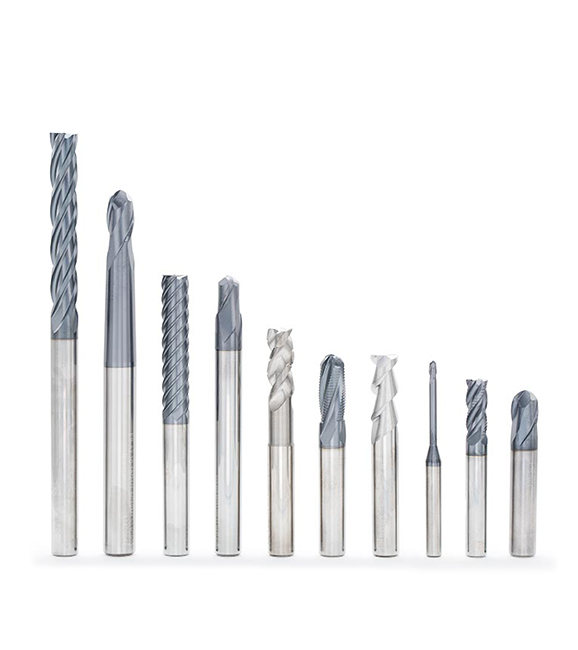
SolidMeister – unsere breite Palette an Schaftfräsern aus Vollhartmetall steigert Ihre Bearbeitungseffizienz und Stabilität in einem breiten Spektrum von Anwendungen

Anwendungen & Funktionen
Anwendungen
Eigenschaften
Große Auswahl an Schaftfräsern aus Vollhartmetall für verschiedene Anwendungen
Schaftfräser & Sorten aus Vollhartmetall
Schaftfräser aus Vollhartmetall
FinishMeister
- Kombination von Schrupp- und Schlichtkanten
- Schruppen und Schlichten zur gleichen Zeit
VariableMeister
- Variable Steigungskonfiguration
- Hervorragende Ratterdämpfungseigenschaften
FeedMeister
- Für Hochvorschubfräsen
- Die neuesten Werkzeuge aus Vollkeramik
Wichtigste Sorten
AH725
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- Gutes Gleichgewicht zwischen Verschleiß- und Spanfestigkeit
- Geeignet für die Bearbeitung von Stahl und rostfreiem Stahl unter allgemeinen Schnittbedingungen
GH730
![]()
![]()
![]()
- Hohe Verschleißfestigkeit
- Geeignet für Drehlösungen und Stechen bei niedriger Geschwindigkeit
KS15F
![]()
Standard Schnittbedingungen
VariableMeister
Slotting / Roughing (ae = 0.4 x D or over)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap (Slotting) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 140 – 180 | 0.03 – 0.045 | 0.035 – 0.055 | 0.05 – 0.07 | 2xD |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 150 | 0.025 – 0.04 | 0.035 – 0.055 | 0.05 – 0.07 | 2xD | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 60 – 100 | 0.025 – 0.045 | 0.035 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.065 | 1xD |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 200 HB | 80 – 180 | 0.025 – 0.05 | 0.035 – 0.065 | 0.05 – 0.075 | 2xD |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 300 – 750 | 0.025 – 0.05 | 0.035 – 0.065 | 0.035 – 0.09 | 2xD |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 20 – 50 | 0.025 – 0.04 | 0.03 – 0.05 | 0.035 – 0.085 | 1xD |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 20 – 30 | 0.01 – 0.02 | 0.02 – 0.04 | 0.03 – 0.06 | 0.5xD |
Semi-finishing / Shouldering (ae = 0.1~0.4 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 150 – 220 | 0.035 – 0.075 | 0.075 – 0.09 | 0.085 – 0.1 | 2xD |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 160 | 0.025 – 0.065 | 0.05 – 0.09 | 0.055 – 0.09 | 2xD | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 80 – 130 | 0.03 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.06 | 0.05 – 0.065 | 2xD |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 130 – 220 | 0.035 – 0.065 | 0.05 – 0.075 | 0.075 – 0.09 | 2xD |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 850 | 0.05 – 0.075 | 0.075 – 0.1 | 0.075 – 0.1 | 2xD |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 40 – 60 | 0.035 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.065 | 0.04 – 0.065 | 2xD |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 30 – 70 | 0.015 – 0.045 | 0.03 – 0.05 | 0.05 – 0.075 | 2xD |
Finishing (feed rate depending on required accuracy) / High feed machining at low depth of cut (ae = 0.05~0.1 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 170 – 280 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 0.085 – 0.1 | 0.1 – 0.125 | apmax |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 110 – 220 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 0.085 – 0.1 | 0.1 – 0.125 | apmax | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 100 – 160 | 0.035 – 0.055 | 0.05 – 0.065 | 0.055 – 0.075 | apmax |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 180 – 280 | 0.04 – 0.075 | 0.075 – 0.08 | 0.08 – 0.1 | apmax |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 900 | 0.055 – 0.09 | 0.085 – 0.125 | 0.125 – 0.18 | apmax |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 50 – 70 | 0.04 – 0.065 | 0.05 – 0.075 | 0.075 – 0.11 | apmax |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 40 – 80 | 0.025 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.065 | 0.06 – 0.08 | apmax |
· When the depth of cut (ae) is closer to the upper limit, please start with a lower limit value of cutting speed (Vc).
· Please set the cutting speed and the feed rate lower for the items with long slot according to how chattering occurs.
· While air blow is recommended, water-soluble coolant will be good for stainless steel, titanium alloy, and heat-resistant alloy.
· When chattering occurs with low rigid machines or settings, reduce cutting speed and feed at an equal rate.
· When chattering occurs with long tool overhang, reduce cutting speed and feed by 20 to 40%.
FinishMeister / ShredMeister
Slotting / Roughing (ae = 0.4 x D or over)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap (Slotting) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 140 – 180 | 0.035 – 0.055 | 0.045 – 0.07 | 0.06 – 0.0825 | 2xD |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 150 | 0.03 – 0.045 | 0.045 – 0.07 | 0.06 – 0.0825 | 2xD | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 60 – 100 | 0.03 – 0.055 | 0.045 – 0.06 | 0.05 – 0.0675 | 1xD |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 200 HB | 80 – 180 | 0.03 – 0.06 | 0.045 – 0.08 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 2xD |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 300 – 750 | 0.03 – 0.06 | 0.045 – 0.08 | 0.04 – 0.105 | 2xD |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 20 – 50 | 0.03 – 0.045 | 0.04 – 0.06 | 0.04 – 0.105 | 1xD |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 20 – 30 | 0.015 – 0.025 | 0.025 – 0.07 | 0.06 – 0.075 | 0.5xD |
Semi-finishing / Shouldering (ae = 0.1~0.4 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 150 – 220 | 0.045 – 0.09 | 0.09 – 0.11 | 0.1 – 0.12 | 2xD |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 160 | 0.03 – 0.075 | 0.06 – 0.1 | 0.065 – 0.105 | 2xD | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 80 – 130 | 0.035 – 0.06 | 0.055 – 0.07 | 0.06 – 0.075 | 2xD |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 130 – 220 | 0.045 – 0.075 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 0.09 – 0.105 | 2xD |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 850 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 0.09 – 0.12 | 0.12 – 0.15 | 2xD |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 40 – 60 | 0.045 – 0.06 | 0.055 – 0.07 | 0.075 – 0.12 | 2xD |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 30 – 70 | 0.02 – 0.055 | 0.045 – 0.07 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 2xD |
Finishing (feed rate depending on required accuracy) / High feed machining at small width of cut (ae = 0.05~0.1 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 170 – 280 | 0.075 – 0.11 | 0.11 – 0.12 | 0.12 – 0.15 | apmax |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 110 – 220 | 0.075 – 0.11 | 0.11 – 0.12 | 0.12 – 0.15 | apmax | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 100 – 160 | 0.045 – 0.07 | 0.06 – 0.075 | 0.065 – 0.09 | apmax |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 180 – 280 | 0.05 – 0.09 | 0.09 – 0.1 | 0.09 – 0.12 | apmax |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 900 | 0.065 – 0.11 | 0.11 – 0.15 | 0.15 – 0.22 | apmax |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 50 – 70 | 0.055 – 0.075 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 0.09 – 0.12 | apmax |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 40 – 80 | 0.03 – 0.06 | 0.05 – 0.09 | 0.075 – 0.105 | apmax |
· When the depth of cut (ae) is closer to the upper limit, please start with a lower limit value of cutting speed (Vc).
· While air blow is recommended, water-soluble coolant will be good for stainless steel, titanium alloy, and heat-resistant alloy.
· When chattering occurs with low rigid machines or settings, reduce cutting speed and feed at an equal rate.
· When chattering occurs with long tool overhang, reduce cutting speed and feed by 20 to 40%.
SolidMeister / EcoMeister
Slotting / Roughing
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap (Slotting) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 140 – 180 | 0.025 – 0.035 | 0.03 – 0.045 | 0.04 – 0.055 | 1xD |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 150 | 0.02 – 0.03 | 0.03 – 0.045 | 0.04 – 0.055 | 1xD | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 60 – 100 | 0.02 – 0.035 | 0.03 – 0.04 | 0.035 – 0.045 | 0.5xD |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 200 HB | 80 – 180 | 0.02 – 0.04 | 0.03 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.06 | 1xD |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 300 – 750 | 0.02 – 0.04 | 0.03 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 | 1xD |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 20 – 50 | 0.02 – 0.03 | 0.02 – 0.03 | 0.03 – 0.07 | 0.25xD |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 20 – 30 | 0.01 – 0.015 | 0.02 – 0.045 | 0.04 – 0.05 | 0.2xD |
Semi-finishing / Shouldering (ae = 0.1-0.4 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 150 – 220 | 0.03 – 0.06 | 0.06 – 0.07 | 0.07 – 0.08 | 2xD |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 160 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.065 | 0.045 – 0.07 | 2xD | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 80 – 130 | 0.025 – 0.04 | 0.035 – 0.045 | 0.04 – 0.05 | 2xD |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 130 – 220 | 0.03 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.06 | 0.06 – 0.07 | 2xD |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 850 | 0.04 – 0.06 | 0.06 – 0.08 | 0.08 – 0.1 | 2xD |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 40 – 60 | 0.03 – 0.04 | 0.035 – 0.05 | 0.05 – 0.08 | 2xD |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 30 – 70 | 0.015 – 0.035 | 0.035 – 0.055 | 0.045 – 0.06 | 2xD |
Finishing (feed rate depending on required accuracy) / High feed machining at low depth of cut (ae = 0.05-0.1 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 170 – 280 | 0.05 – 0.07 | 0.07 – 0.08 | 0.08 – 0.1 | apmax |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 110 – 220 | 0.05 – 0.07 | 0.07 – 0.08 | 0.08 – 0.1 | apmax | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 100 – 160 | 0.03 – 0.045 | 0.04 – 0.05 | 0.045 – 0.06 | apmax |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 180 – 280 | 0.035 – 0.06 | 0.06 – 0.065 | 0.065 – 0.08 | apmax |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 900 | 0.045 – 0.07 | 0.07 – 0.1 | 0.1 – 0.15 | apmax |
 |
Titanium alloy | – 40 HRC | 50 – 70 | 0.035 – 0.05 | 0.04 – 0.06 | 0.06 – 0.085 | apmax |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 40 – 80 | 0.02 – 0.04 | 0.04 – 0.06 | 0.05 – 0.07 | apmax |
· When the depth of cut (ae) is closer to the upper limit, please start with a lower limit value of cutting speed (Vc).
· The items with long slot (2xD or over) and the items with 5 cutting edges or more are not suitable for slotting operation.
· When using AH750, reducing cutting speed by 20 to 30% is effective for extending tool life.
· While air blow is recommended, water-soluble coolant will be good for stainless steel, titanium alloy, and heat-resistant alloy.
· When chattering occurs with low rigid machines or settings, reduce cutting speed and feed at an equal rate.
· When chattering occurs with long tool overhang, reduce cutting speed and feed by 20 to 40% (Variable/FinishMeister is recommended for such operations).
· In slotting of high hardened steel, heat-resistant alloy, and some types of stainless steel, start with ap=0.2xD and increase the value gradually while checking the status of
the operation.
· In shoulder milling of high hardened steel and heat-resistant alloy, the cutting width should be started at ae=0.05xD and increase the value gradually while checking the
status of the operation.
· The items with many cutting edges are good for finishing and high feed machining of small width of cut.
· VariableMeister is suitable for machining large depth of cut.
· Low feed in finishing is recommended for good surface roughness.
ball nose endmill
Shape machining (Roughing to semi-finishing)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø3 – ø6 | ø8 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 125 – 200 | 0.02 – 0.055 | 0.04 – 0.08 | 0.06 – 0.11 | 0.05 – 0.12 x D |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 100 – 150 | 0.01 – 0.035 | 0.03 – 0.05 | 0.045 – 0.06 | 0.04 – 0.1 x D | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 110 | 0.015 – 0.03 | 0.03 – 0.04 | 0.05 – 0.06 | 0.05 – 0.1 x D |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 150 – 180 | 0.03 – 0.06 | 0.06 – 0.09 | 0.09 – 0.12 | 0.08 – 0.15 x D |
 |
Titanium alloys | – 40 HRC | 30 – 60 | 0.008 – 0.02 | 0.025 – 0.03 | 0.03 – 0.04 | 0.04 – 0.08 x D |
| Heat-resistant alloys | – 40 HRC | 20 – 30 | 0.008 – 0.02 | 0.025 – 0.03 | 0.03 – 0.04 | 0.04 – 0.08 x D | |
 |
Hardened steel | – 49 HRC | 70 – 80 | 0.008 – 0.02 | 0.025 – 0.03 | 0.03 – 0.04 | 0.04 – 0.08 x D |
| Hardened steel | 50 – 60 HRC | 30 – 40 | 0.005 – 0.008 | 0.007 – 0.013 | 0.009 – 0.02 | 0.03 – 0.06 x D | |
Finishing
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø3 – ø6 | ø8 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | |||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 170 – 280 | 0.017 – 0.046 | 0.034 – 0.068 | 0.051 – 0.094 | 0.02 x D |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 120 – 165 | 0.008 – 0.03 | 0.025 – 0.043 | 0.038 – 0.051 | 0.01 x D | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 150 | 0.012 – 0.026 | 0.025 – 0.034 | 0.042 – 0.051 | 0.01 x D |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 200 – 220 | 0.025 – 0.051 | 0.051 – 0.077 | 0.076 – 0.102 | 0.03 x D |
 |
Titanium alloys | – 40 HRC | 30 – 60 | 0.007 – 0.017 | 0.021 – 0.026 | 0.025 – 0.034 | 0.01 x D |
| Heat-resistant alloys | – 40 HRC | 20 – 30 | 0.007 – 0.017 | 0.021 – 0.026 | 0.025 – 0.034 | 0.01 x D | |
 |
Hardened steel | – 49 HRC | 100 | 0.007 – 0.017 | 0.021 – 0.026 | 0.025 – 0.034 | 0.01 x D |
| Hardened steel | 50 – 60 HRC | 40 – 50 | 0.004 – 0.007 | 0.006 – 0.011 | 0.007 – 0.017 | 0.01 x D | |
· When using AH750, reducing cutting speed by 20 to 30% is effective for extending tool life.
· While air blow is recommended, water-soluble coolant will be good for stainless steel, titanium alloy, and heat-resistant alloy.
· When chattering occurs with low rigid machines or settings, reduce cutting speed and feed at an equal rate.
· When chattering occurs with long tool overhang, reduce cutting speed and feed by 20 to 40% (VariableMeister is recommended for such operations).
High Feed Endmill
Shape machining (roughing) TEFF**N4…
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | ||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 140 – 180 | 0.25 – 0.48 | 0.35 – 0.67 | 0.52 – 0.9 |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 120 – 130 | 0.2 – 0.28 | 0.3 – 0.38 | 0.43 – 0.57 | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 120 | 0.25 – 0.3 | 0.35 – 0.43 | 0.52 – 0.6 |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 160 – 180 | 0.3 – 0.45 | 0.45 – 0.6 | 0.6 – 0.8 |
 |
Hardened steel | – 49 HRC | 100 | 0.16 – 0.2 | 0.25 – 0.33 | 0.4 – 0.48 |
| Hardened steel | 50 – 60 HRC | 60 – 80 | 0.1 – 0.16 | 0.16 – 0.3 | 0.2 – 0.45 | |
Shape machining (roughing) TCFF**A3…
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø6 – ø8 | ø10 – ø12 | ø16 – ø20 | ||||
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 250 – 1000 | 0.1 – 0.15 | 0.17 – 0.19 | 0.23 – 0.25 |
| Ductile cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 250 – 1000 | 0.1 – 0.15 | 0.17 – 0.19 | 0.23 – 0.25 | |
| Malleable cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 250 – 1000 | 0.1 – 0.15 | 0.17 – 0.19 | 0.23 – 0.25 | |
 |
Non-ferrous metal / Graphite | – | 500 – 1500 | 0.1 – 0.15 | 0.17 – 0.19 | 0.23 – 0.25 |
 |
Nickel based alloy | – | 250 – 1000 | 0.1 – 0.13 | 0.15 – 0.18 | 0.20 – 0.22 |
High speed machining generates heat in the tool and chuck holder.
Thermal expansion of the holder will often lead to tool damage. Use an air coolant during machining to cool the tool holder.
Milling chucks are recommended for the toolholder to be used.
*Use the above corner radius values (RE) for programming.
toroidal endmill
Semi-finishing / Shouldering (ae = 0.1-0.4 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø2 | ø3 | ø4 | ø6 | ||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 150 – 220 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 160 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 80 – 130 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 130 – 220 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 850 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Titanium alloy | – | 40 – 60 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 30 – 70 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
Slotting / Roughing
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø2 | ø3 | ø4 | ø6 | ||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 140 – 180 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 70 – 150 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 60 – 100 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 200 HB | 80 – 180 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 300 – 750 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Titanium alloy | – | 20 – 50 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 20 – 30 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
Finishing (feed rate depending on required accuracy) / High feed machining at low depth of cut (ae = 0.05-0.1 x D)
| ISO | Workpiece material | Hardness | Vc (m/min) | fz (mm/t) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø2 | ø3 | ø4 | ø6 | ||||
 |
Carbon steel | – 300 HB | 170 – 280 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
| Alloy steel | – 300 HB | 110 – 220 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 | |
 |
Stainless steel | – 200 HB | 100 – 160 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Cast iron | 150 – 250 HB | 180 – 280 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Aluminium alloy | – | 350 – 900 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Titanium alloy | – | 50 – 70 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
 |
Hardened steel | – 60 HRC | 40 – 80 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.01 – 0.04 | 0.02 – 0.05 | 0.03 – 0.07 |
· When the depth of cut (ae) is closer to the upper limit, please start with a lower limit value of cutting speed (Vc).
· The items with long slot (2xD or over) is not suitable for slotting operation.
· While air blow is recommended, water-soluble coolant will be good for stainless steel, titanium alloy, and heat-resistant alloy.
· When chattering occurs with low rigid machines or settings, reduce cutting speed and feed at an equal rate.
· When chattering occurs with long tool overhang, reduce cutting speed and feed by 20 to 40%.
· In slotting of high hardened steel, heat-resistant alloy, and some types of stainless steel, start with ap=0.2xD and increase the value gradually while checking
the status of the operation.
· In shoulder milling of high hardened steel and heat-resistant alloy, the cutting width should be started at ae=0.05xD and increase the value gradually while
checking the status of the operation.
· Low feed in finishing is recommended for good surface roughness.
Barrel endmill
| ISO | Workpiece materials | Hardness | Priority | Grade | Cutting speed Vc (m/min) | Feed per tooth: fz (mm/t) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tool diameter: DC (mm) |
|||||||||
| 8 | 10 | 12 | |||||||
 |
Low carbon steel SS400, S15C, etc. E275A, C15E4, etc., C15E, etc. |
– 200 HB | First choice | AH710 | 210 – 300 | 0.04 – 0.08 | 0.05 – 0.1 | 0.06 – 0.12 | |
| Carbon steel, Alloy steel S55C, SCM440, etc. C55, 42CrMo4, etc. |
– 300 HB | First choice | AH710 | 160 – 240 | 0.024 – 0.064 | 0.03 – 0.08 | 0.036 – 0.096 | ||
| Prehardened steel PX5, NAK80, etc. |
30 – 40 HRC | First choice | AH710 | 130 – 200 | 0.016 – 0.064 | 0.02 – 0.08 | 0.024 – 0.096 | ||
 |
Stainless steel SUS304, SUS316, etc. X5CrNi18-9, X5CrNiMo17-12-3, etc. |
– | First choice | AH710 | 60 – 110 | 0.016 – 0.056 | 0.02 – 0.07 | 0.024 – 0.084 | |
 |
Grey cast iron FC250, FC300, etc. 250, 300, etc., GG25, GG30, etc. |
150 – 250 HB | First choice | AH710 | 150 – 275 | 0.04 – 0.08 | 0.05 – 0.1 | 0.06 – 0.12 | |
| Ductile cast iron FCD400, etc. |
150 – 250 HB | First choice | AH710 | 150 – 200 | 0.04 – 0.08 | 0.05 – 0.1 | 0.06 – 0.12 | ||
 |
Titanium alloys Ti-6AI-4V, etc. |
– | First choice | AH710 | 60 – 90 | 0.016 – 0.032 | 0.02 – 0.04 | 0.024 – 0.048 | |
| Heat-resistant alloys Inconel718, etc. |
– | First choice | AH710 | 20 – 35 | 0.016 – 0.032 | 0.02 – 0.04 | 0.024 – 0.048 | ||
 |
Hard material | SKD61, etc. X40CrMoV5-1, etc. |
40 – 50 HRC | First choice | AH710 | 40 – 80 | 0.008 – 0.024 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.012 – 0.036 |
| SKD11, etc. X153CrMoV12, etc. |
50 – 60 HRC | First choice | AH710 | 40 – 80 | 0.008 – 0.024 | 0.01 – 0.03 | 0.012 – 0.036 | ||
Weitere Informationen zu diesem Produkt finden Sie in unserem Online-Katalog oder im Produktbericht, den Sie herunterladen können: